The history of the United States is a vast and complex narrative that spans several centuries, marked by significant events, cultural shifts, and pivotal moments. It is a story of immigration, struggle, innovation, and transformation. This brief overview aims to provide a concise yet comprehensive introduction to American history in English.

Early Indigenous Cultures and European Colonization:
Long before European settlers arrived, North America was home to diverse indigenous cultures, each with its own distinct traditions, languages, and societies. The arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1492, although he never actually reached what would become the United States, sparked widespread European interest in the New World. Spanish explorers followed, seeking wealth in the form of gold and silver. The early 16th century saw French, Dutch, and English attempts at colonization as well, with Jamestown, Virginia (1607) and Plymouth Colony (1620) being among the first successful English settlements. These early colonies struggled for survival, but they laid the groundwork for future expansion.
Revolutionary Era and Independence:
By the mid-18th century, tensions between the thirteen American colonies and British rule had escalated. Resentment over taxation without representation, exemplified by the Stamp Act (1765) and the Townshend Acts (1767), fueled revolutionary sentiments. The Boston Tea Party in 1773 was a direct protest against British taxation policies. In 1776, the Declaration of Independence was adopted, declaring the colonies' freedom from Britain. The subsequent Revolutionary War (1775-1783) resulted in an American victory with the Treaty of Paris in 1783, recognizing the sovereignty of the United States.
The Formation of a New Nation:
In 1787, the Constitutional Convention met to create a new framework for government. The U.S. Constitution, ratified in 1789, established a federal system of government with three branches—the legislative (Congress), executive (President), and judicial (Supreme Court)—designed to ensure checks and balances. The Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments to the Constitution, enshrine fundamental liberties such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial.
Expansion Westward and Antebellum Period:
Throughout the 19th century, the U.S. expanded rapidly across the continent through territorial acquisitions and westward migration. The Louisiana Purchase (1803) doubled the size of the nation. However, this period also saw growing tensions over slavery. The institution of slavery became a major divisive issue, leading to regional conflicts and ultimately the Civil War (1861-1865). President Abraham Lincoln's leadership during the war and his Emancipation Proclamation in 1863 marked turning points towards ending slavery. The post-war Reconstruction era aimed to rebuild the South and integrate formerly enslaved people into society.
Industrialization and the Progressive Era:
The late 19th century witnessed rapid industrialization, transforming the U.S. into a leading global economy. Cities grew, technological advancements flourished, and immigration surged from Europe and Asia. However, this era also brought challenges like labor disputes, urban poverty, and social inequality. The Progressive Era (1890s-1920s) emerged in response, with reformers advocating for social justice, economic regulation, and political integrity. Figures like Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson pushed for antitrust laws, women's suffrage, and labor rights protections.
World Wars and the Twentieth Century:
The 20th century was marked by two world wars and the rise of the U.S. as a superpower. The Great Depression (1929-1939) tested the nation's resilience before World War II (1939-1945) solidified America's position on the world stage. The post-war period saw economic prosperity under policies like the G.
I. Bill and the Marshall Plan. The 1950s and 1960s were defined by Cold War dynamics with the Soviet Union, civil rights struggles led by figures like Martin Luther King Jr., and the space race culminating in Neil Armstrong's moon landing in 196
9.By the late 20th century, the U.S. faced new challenges including economic recessions, terrorism, and debates over foreign policy and national identity.
Conclusion:
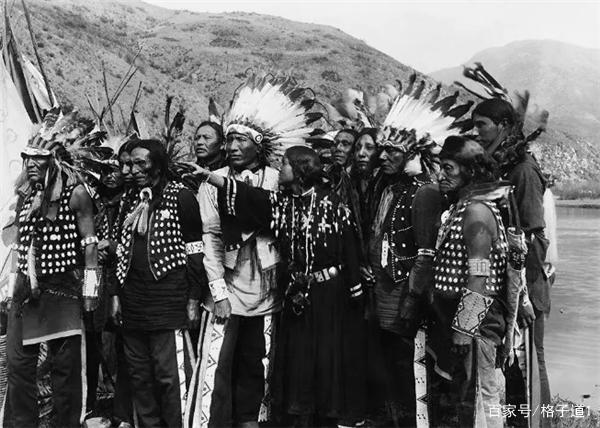

The history of the United States is a testament to its people's resilience, adaptability, and pursuit of democratic ideals. From its early colonial beginnings to becoming a global superpower, the nation has continually evolved, facing internal divisions and external threats while striving for progress and equality. Today, the U.S. stands as a symbol of both opportunity and ongoing challenge in a rapidly changing world.
标签:#福地阅读网









评论列表